3.1.2. Power dissipated by the LED diode
The power LED is determined by the voltage drop across the terminals and the current device according to the expression:
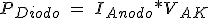
The following figure shows the power LED based on the anode current by a constant power supply. By varying the current between 0 and the rated 900 mA, the power loss shows a linear trend because the voltage drop across the diode is almost constant. Again there was a noticeable difference between the data provided by the manufacturer and the actual value of power, 10 W and 8.3 W respectively.
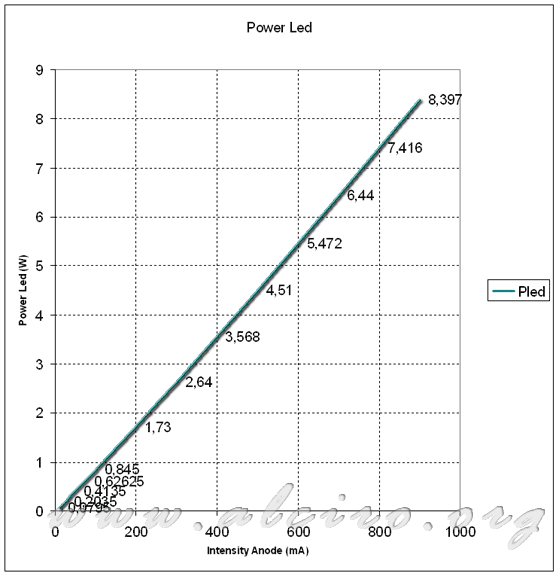
Power LED 10W
3.1.3. Led diode temperature
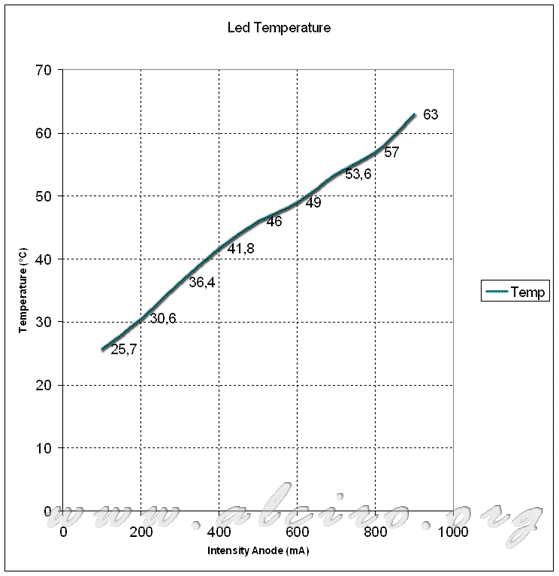
Temperature LED 10W
The temperature reached by the LED is very important in determining the life of the device. The following figure shows the temperature of the diode as a function of the anode. To prevent damage to the diode, this has been placed on a radiator with a heat transfer coefficient of 5 º C / W. The temperature was measured directly on the wings of the sink.
The graph shows an almost linear curve equivalent to the power supplied. Between 100mA and 600mA the low system temperature of 25 º C to 50 º C, between 600mA and 900mA the temperature rises to 63 º C, not being a critical temperature for a power semiconductor. If the temperature exceeds 70 ° C would have to adopt means to cool the LED more efficiently.
Test conditions:
- Radiator thermal resistance: 5 º C / W
- Ambient temperature: 20 º C
To check the temperature power relationship, we can apply the equation of heat resistance.
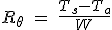
- Ts = Temperature in ° C sink
- Ta = Ambient temperature in ° C
- W = power dissipated in Watts
If we find the value of the power loss equation is:
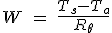
For 900mA rated temperature is 63 º C with an ambient temperature of 20 º C, the power dissipation is:
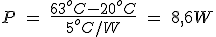
The power obtained from the temperature coincides with that provided so that you can validate the results obtained in the current-temperature plot.
Temperature can be improved if we use a radiator with a lower thermal resistance. For example with a radiator Rθ = 3 º C / W:
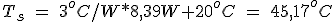
3.1.4. Conclusions
The actual characteristics of LED are below those indicated by the manufacturer.
The temperature of the device is not very high, and can be improved by using a sink to a lower thermal resistance.
The radiation angle is good, I can see that the value specified by the manufacturer 160 º is correct.
A lack of instruments to mediate the light radiation can be entirely subjective observation. You could say that the radiation emitted by the LED power is equivalent to a 10W incandescent lamp of about 40-50W.







