2.1.3.3. Microstep sequence
The length of one step of a stepper motor can be divided into small increments of rotor position, known as 'microsteps', making a special control on the excitation windings of the phases.
If we consider that for a hybrid engine peak static torque produced is proportional to the current through the phases (Figure 3.3) and the torque curve sine varies with the position of rotor torque is obtained:
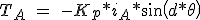\\ T_B\ =\ -K_p*i_B*sin(d*\theta-\frac{\pi }{2} )) (3.8)
(3.8)
K p is the constant of proportionality between the pair obtained and the intensity of phase B i A yi.
Operating in a conventional manner, the winding is excited with rated current positive or negative, resulting in a step-length π / (2 * d) for each change of the excitation. To operate in microstep driver of each phase should generate a current in a fraction of the nominal current, I:
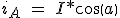\\ i_B\ =\ I*cos(a-\frac{\pi }{2})) (3.9)
(3.9)
total torque produced by the engine well determined by:
![Equation total torque produced by the motor in microstep T\ =\ T_A+T_B\ =\ -K_p*I*\left[ sin(d*\theta )*cos(a)+sin(d*\theta -\frac{\pi }{2})*cos(a-\frac{\pi }{2}) \right]\\ =\ -K_p*I*sin(d*\theta -a)](http://www.alciro.org/cgi/tex.cgi?T\ =\ T_A+T_B\ =\ -K_p*I*\left[ sin(d*\theta )*cos(a)+sin(d*\theta -\frac{\pi }{2})*cos(a-\frac{\pi }{2}) \right]\\ =\ -K_p*I*sin(d*\theta -a)) (3.10)
(3.10)
and the position of zero torque equilibrium is Θ = a / p. A microstep is when there is a variation of the current flowing through the windings, on the other hand, the number of microsteps occurring within one step length is determined by the number of variations that give to the rated current. And the length of NL microstep with current levels is:
\ =\ \frac{(rotor\ tooth\ pitch)}{2*N_L}) (3.11)
(3.11)
A hybrid with a 1.8 º per step angle is an angle of 7.2 ° at the distance of a tooth (rotor tooth pitch). With a driver to control power levels can be obtained microsteps lengths of 0.36 º.
For the conventional full step operation the equilibrium position is defined by the alignment of the teeth of the rotor and stator regardless of current level. On the contrary, the position of the microstep is very critical and depends on the current flowing through the coils, an error in the rotor is moved to a position error.
The adoption of excitement Microstepping provides a number of advantages over conventional. A typical resolution is 20 microstep per step. A stepper motor operating in full step has a mechanical resonance (see chapter 3.2.3) but microsteps eliminates this problem. The major disadvantage is the cost of the driver, it also reduces static peak torque produced by the engine, but with little significant.







