5.1.9. Example of calculating torque motor pull-in start
Example 2. Find the pull-in torque necessary to start the motor of Example 1 at a rate of 100 steps steps / s. To contrast the characteristics of torque / speed.
When the engine starts at a ratio of specific steps, the acceleration produced is very high. If the inertia of the system are large, may be the case that the engine has sufficient torque to start with this because of steps, being necessary to start at a lower speed. Figure 5.22 shows the curve speed / time to run at a ratio determined steps. At the time the motor receives power from the first step, it is at rest with zero velocity. Obviously the engine can not start instantly and be at the posted speed, it takes time to reach that speed. This delay is often the equivalent of two steps, we determine the acceleration of the boot.
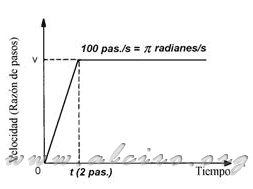
Figure 5.22. Response from the engine to run at a speed.
The time of two steps if the motor excitation sequence is 100 steps / s will be 2 pas. / 100 pas. / S = 0.02 s, then the acceleration will be determined by,
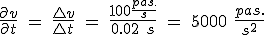 (5.46)
(5.46)
transforming to angular acceleration.
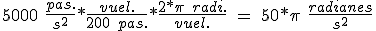 (5.47)
(5.47)
You can also apply directly to the angular velocity.
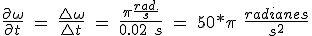 (5.48)
(5.48)
Substituting in equation 5.45 we get the torque needed to boot the system at a rate of 100 steps / s.
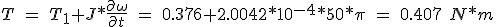 (5.49)
(5.49)
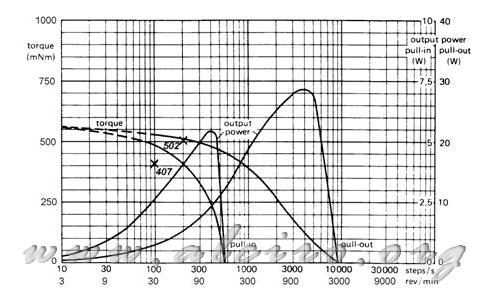
Figure 5.23. Curve pull-in for a hybrid engine from 1.8 º to the situation of torque to boot steps at a rate of 100 steps / s (407 mN * m) and 200 steps / s (502 mN * m).
If the pair obtained is situated in the characteristic curve of torque / speed pull-in (Figure 5.23), we can see that the speed of 100 steps / s the pair that provides the engine is higher than necessary, thus the system can start this right steps. But if we try to start at 200 steps / s the acceleration would be to 20000 step / s 2 = 200 * π radians / s 2 and the required torque is 502 mN * m, which is located in the pull-in curve to the rate of 200 steps / s comes out of it, being impossible for the engine to start.







