4.1.3. Half-step sequence (half step)
This sequence is the combination of the two mentioned above, alternating a full step position with another wave, getting the rotor to stabilize the positions aligned with the stator as in intermediate positions. Trading excitation sequence half step, the number of steps per revolution is doubled and consequently the pitch angle is divided equally by two. Figure 4.8 shows the position of the rotor about the stator of a three phase motor. The combination of the two sequences in an instant makes the two phases are fed and the next only one. The result is that the pair obtained is inferior to that provided excitation full step, but higher than the excitation wave.
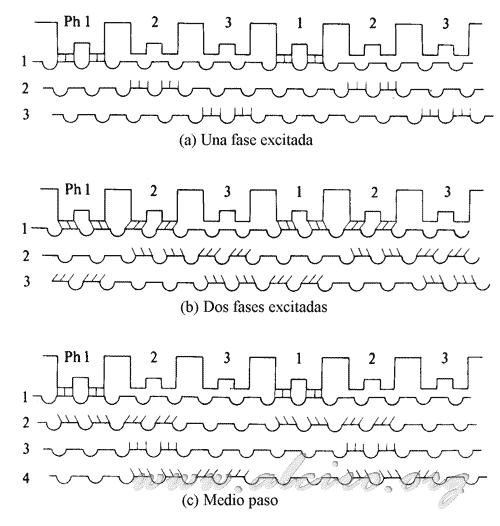
Figure 4.6. Comparison of the positions of the rotor teeth and stator of a variable reluctance motor three-phase sequence excitation of an active phase, two phase additive and a half-step
The loss of torque to work in half steps can be offset by increasing the flow of the active phase winding by a factor of (2 1 / 2). This factor applies to the rated current work we indicate the characteristics of the motor manufacturer. They always refer to the maximum current per phase with both windings excited, and excitation sequence full step. The increase of the factor (2 1 / 2) of the current, double the power dissipated in the active phase. Then the total power dissipated is approximately equal to the full step operation, since no active phase does not dissipate power. With the formation of wave excitation (2 1 / 2) yields a pair of 95% compared to full step system.
Table 4.3 indicates the excitation sequence of half steps. The waveforms for forward and reverse are illustrated in Figure 4.7 and 4.8.
| Clock | Steps | Phase A | Phase B |
| Ref | Ref | + I | + I |
| 1 | ½ | 0 | + I |
| 2 | 1 | - I | + I |
| 3 | 1 ½ | - I | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | - I | - I |
| 5 | 2 ½ | 0 | - I |
| 6 | 3 | + I | - I |
| 7 | 3 ½ | + I | 0 |
| 8 | 4 | + I | + I |
Table 4.3. Sequence of excitation of a half-step (half step).
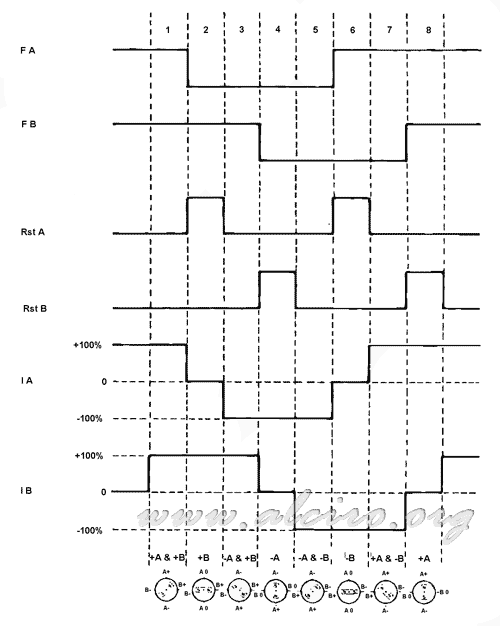
Figure 4.7. Sequence step forward in the middle (half step).
Working with half steps makes the increase in half steps is half that in full step, reducing the oscillation in response to a step. This minimizes the effects of mechanical resonance occurring in the engine at certain frequency regions of way. Figure 4.9 shows a comparison of dynamic characteristics curves torque / speed for the excitation sequence in full step, half-step and half step wave shape (2 1 / 2). It also shows the waveform of current through an exciting phase for a half-step and half step wave shape.
All you have to avoid the formation of wave excitation with (√ 2) is to stop the motor current limit conditions and in a position half-step. Because the heat dissipation of the whole is concentrated in a single winding.
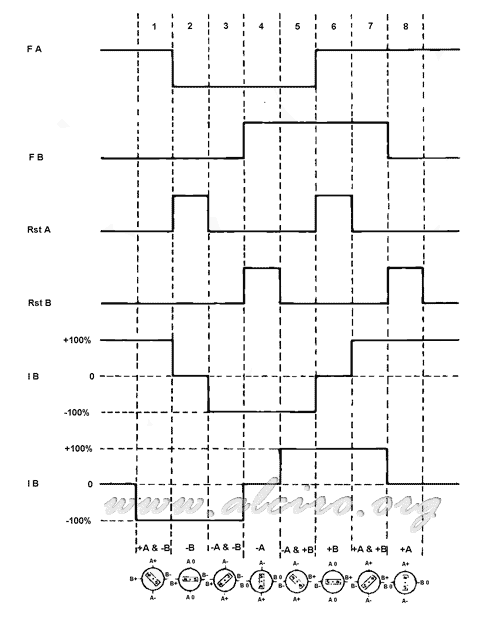
Figure 4.7. Sequence half-step back (half step).
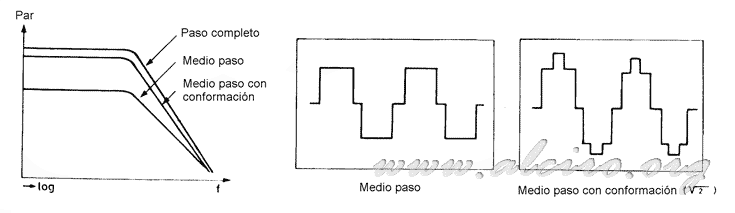
Figure 4.9 Torque produced by the different excitation sequences. Waveforms of the excitation intensity for a half-step and half step conformation.







